Natural conditions and resources of Luc Ngan district
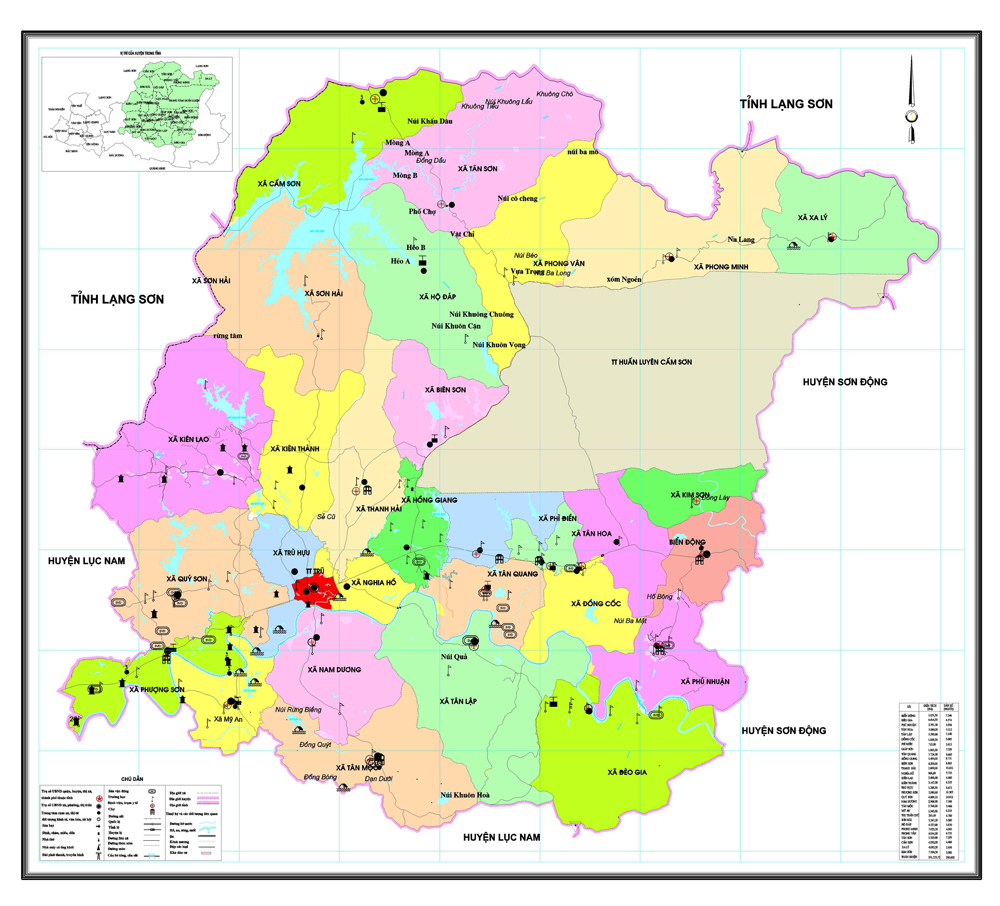
1. Natural conditions
1.1. Geographical location:
Luc Ngan is a mountainous district of Bac Giang province which is located on the National Highway No 31 with the administrative boundaries as follow:
- It is adjacent to Chi Lang and Huu Lung district, Lang Son province to the North;
- It is adjacent to Luc Nam district, Bac Giang province to the West and South;
- It is adjacent to Son Dong district, Bac Giang province to the East.
The district center is 40 km far from Bac Giang city with total land area of 101,223.71 hectares and 30 administrative units divided into 2 separate zones including the lower zone consisting of 17 communes and 1 town and upper zone with 12 communes.
1.2. Topography:
The mountainous district of Luc Ngan has the terrain divided into 2 separate zones including high mountainous and low hilly zones.
a. The high mountainous areas: this type of terrain accounts for nearly 60 percent of the natural land area of the district including 12 communes namely Son Hai, Cam Son, Tan Son, Ho Dap, Phong Minh, Sa Ly, Phong Van, Kim Son, Phu Nhuan, Deo Gia, Tan Lap and Tan Moc. This region is heavily separated with high slope, the average height ranges from 300 to 400 metre, the lowest is 170 metre compared to the sea level. Of which, high mountains with slope of over 25-degree account for over 60 percent of the natural area in the region mainly covered by natural forests. The population in this zone are mainly ethnic minorities with low density, about 110 persons per square kilometre. The economy of this zone is undeveloped with big potential to develop forest economy, livestock and fruit cultivation. In the future, it can develop tourism in the areas of Cam Son and Khuon Than Lakes.
b. The low hilly areas: this type of terrain is featured in the other 17 communes and 1 town with the land area accounting for 40 percent of the district’s area. The terrain has medium fragmentation with average height ranging from 80 to 120 metre against the sea level. Most of the land area are gentle hills, some of which are eroded and lack of water source for plantation. However, the soil condition in this area is suitable for fruit trees like persimmon, longan and lychee. Specially, this area has been developed into the biggest lychee cultivation area in northern Vietnam while it also continues to plant crops and develop fruit processing industry. It has big potentials to develop garden ecotourism in the future.
1.3. Climate
Luc Ngan is located in the northeast region of Vietnam, thus it belongs to the monsoon tropical climate region including the climate sub-region featuring climate characteristics of mountainous areas like Lang Son and Thai Nguyen provinces.
- The annual average temperature is 23.5 Celsius degree, the highest in June is 27.8 degree and the lowest in January and February is 18.8 degree.
- The thermal radiation is medium compared to the monsoon tropical climate regions with average sunshine duration of 1,729 hours per year and 4.4 hours per day. The thermal radiation condition is favourable for development of many types of plants.
- The average humidity is 81 percent, the highest is 85 percent and the lowest is 72 percent.
- Storm: this area is impacted by northeast wind at an average speed of 2.2 m/s in winter and it has southeast winds in summer which is rarely affected by storms.
In general, Luc Ngan has low rainfall, less fog with late spring rains, medium humidity and thermal radiation which are favourable for flowering and fruit bearing especially lychee.
1.4. Hydrography:
Luc Ngan has lower rainfall than other areas in Bac Giang province.
According to the district hydro-meteorological station, the climate features of the district are summarized as follow:
The average annual rainfall is 1,321 mm with the highest rainfall is 1,780mm in June, July and August and the lowest rainfall is 912mm in December and January. This is difficult for development of plants and livestock.
1.5. Natural catastrophe:
Luc Ngan district has lowest average rainfall compared to other areas in Bac Giang province. It is a mountainous district with large natural forest area, the terrain is slope from 8 to 15 degree even over 25 degree in some areas, thus it is rarely affected by flood. Otherwise, drought often occurs due to law rainfall and inappropriate irrigation development causing impacts on growth and productivity of the plants. Insects and diseases also occur in some areas in the district. Especially, the district is rarely impacted by storms and earthquake.
Thanks to less natural disaster, the district has favourable conditions for sustainable development. However, it is necessary to strengthen irrigation solutions to reduce impact of drought and pay attention to plant protection, early detecting insect and diseases for timely prevention.
2. Natural resources
2.1. Land resources
Luc Ngan has total natural land area of 101,223.72 hectares. According to the statistics, Luc Ngan has 6 main groups of soil and 14 sub-groups of soil including:
1. The group of alluvial soil covers an area of 2,148.15 hectares, accounting for 2.16 percent of the total land area. Of which, 80 percent of this soil is suitable for crop cultivation of different types and the other 20 percent can be used for 2 crops of rice and 1 crop of veggie.
2. The group of muddy soil covers an area of 18.79 hectares, accounting for 0.02 percent which is in the shallow plains facing flooding. This type of soil can be improved for aquaculture.
3. The ferralit soil group in 700 to 900-metre mountains above the sea level covers an area of 1,728.72 hectares making up for 1.82 percent of the total area. This soil group has high slope with thick layers from 30 to 100 cm which is suitable for forestry development in need of forestation and forest recovery.
4. The ferralit soil group in 200-700m mountains above the sea level covers an area of 23,154.73 hectares, accounting for 24.4 percent of the total land area, mainly in high hills with big slope, which is suitable for forestry development. Some of which at the height of over 200m can be used for perennial fruit trees like longan, persimmon and lychee.
5. The ferralit soil group in lower hilly areas at the height from 25 to 200m covers an area of 56,878.42 hectares, accounting for 59.93 percent of the total land area. This soil group is suitable for forestation and planting industrial and fruit trees such as longan, lychee, persimmon, custard apple especially lychee bearing high economic efficiency.
6. The soil group for rice cultivation covers an area of 5,042 hectares making up for 4.98 percent. This soil group is in plain and terraced fields which is suitable for planting crops like rice, corn, potato, vegetable. However, many areas have been degraded.
Although Luc Ngan is a mountainous district, it has about 10,000 hectares of plain land with slopes ranging from 0 to 8 degree accounting for 10 percent of the natural land area. This is favourable for crop cultivation. If the soil is properly used and improved for high-productivity crop cultivation, it can solve the food problem for the people in the district.
The district has 30 percent of land with the slope from 8 to 25 degree in low hilly areas. This is potential for development of industrial and fruit trees especially lychee, which has been sharply developed. The other 60 percent of land with the slop of over 25 degree is suitable for forestry development.
Luc Ngan district is located in monsoon tropical climate region. Although the annual rainfall is less than other areas in Bac Giang province, it has abundant water resources from Luc Nam river and the lakes of Cam Son and Khuon Than. If it is properly exploited, it will develop a diversified economy in agriculture, industry, trade, service and garden tourism based on the diversified ecosystem of various types of forest trees and fruits with high economic values.
2.2. Water resources
Surface water resources
The Luc Nam river runs across the locality at a length of nearly 45 kilometre from Deo Gia hill to My An and Phuong Son commune. The river runs yearly at a big flow. The average water level in rainy season is about 4.5 metre, the highest food flow is Qmax= 1,300 – 1,400 m3/s and the water flow in dry season is Qmin= 1 m3/s. There are also small streams running across the high communes apart from Luc Nam river.
Apart from Luc Nam river, there are many small streams, lake and pond systems in the district thanks to good irrigation movement to build dams and dykes. Particularly, Cam Son Lake, the biggest in the district covering 2,600 hectares, Khuon Than Lake covering an area of 140 hectares and many other lakes with total area of thousands of hectares in line with the stream system supply a big water reserve meeting people’s demand for production and living.
Underground water resources
The underground water resources: it has not been carefully surveyed and evaluated the underground reserve but after some surveys upon a number of wells in some areas in the district, it can be figured out that the underground water is existed not very deep (at the depth of about 20 to 25 metre) with good water quality which can be used for living purpose in the residential areas.
In general, the water resources in the district has quite good quality and reserve which can meet the demand for production and living. However, due to lower rainfall than other areas, the agricultural cultivation faces numerous difficulties, particularly long drought occurring some years causing the lakes and dykes exhausted seriously affecting crop cultivation and people’s living. Thus, it is necessary to carefully survey the water reserve to build appropriate plans in line with protecting and developing watershed forests to surmount water shortage in dry season.
In general, the water resources in Luc Ngan district from Luc Nam river and the 2 big lakes of Cam Son and Khuon Than and numerous smaller lakes, rivers and streams provide big potentials, thus the district needs to supplement and complete appropriate water system to serve agro-forestry and industrial production and living purpose while implementing exploration and evaluating underground water resources as well as fostering forestation to cover bare hills and mountains to maintain the rain water reserve.
2.3. Forest resources
Luc Ngan is a mountainous district with forestry area of 35,817.85 hectares accounting for 35.38 percent of the total natural land area of the district.
Of which, the production forest area is 16,124.04 hectares making up for 45.01 percent of the total forestry area. The detective forest area is 19,693.81 hectares accounting for 54.98 percent of the total forestry area in the district.
2.4. Mineral resources
Luc Ngan district is home to some precious mineral deposits such as coal, copper and gold. According to an investigation on underground minerals, the district has a coal reserve of about 30,000 tons, copper reserve of 40,000 tons at low concentration, thus it is not exploited for industrial purpose. Besides, Luc Ngan district has a small reserve of gold placer and some other minerals such as stone, gravel, sand and clay which can be exploited to produce construction materials.
2.5. Cultural resources
Luc Ngan is a high mountainous district with total land area of 101,223 hectares and population of 204,041 including 8 ethnic groups in which Kinh ethnic group accounts for 51 percent and other ethnic minority groups like Tay, Nung, San Diu, San Chi, Cao Lan, Dao, Thai, E De and Hoa (Chinese) account for 49 percent. The district has 29 communes and 1 town consisting of 397 vilages and hamlets divided into 2 different areas: the lower area with 17 communes and 1 town and the high and remote area with 12 communes.
In 2006, the district had 202 villages and hamlets recognized cultural villages and 27,226 households recognized cultural families. The people of all ethnic groups in the district are actively working and transferring economic structure to keep pace with the market economy. The district is strongly developing the garden and forest economy with farm production creating special lychee gardens, beautiful ecosystem to attract tourists. This is a cultural resource with rich tradition for promoting its internal force. Luc Ngan has Ha Temple historical relic site ranked as a national relic and another provincial relic in line with numerous natural beautiful landscapes such as Cam Son Lake, Khuon Than Lake, Lang Thum Lake which can be built into tourism sites to serve local people and tourists.
3. Human resources
3.1. Population
The district’s population in 2006 was 204,041 with the national population growth rate is 1.19 percent including 100,729 female accounting for 49.37 percent. It has 44,148 households with 4.62 people per each household on average. The population density is 202 persons per square kilometre including 96.63 percent of rural population and 3.37 percent of urban population showing that the urbanization and industrial and service development in Luc Ngan district is low.
The population is unevenly distributed among the communes in the district. The most crowded commune is Quy Son with 15,167 people followed by Thanh Hai commune with 13,885 people and the commune with smallest population is Sa Ly with 2,681 people.
Table 1: Population scale and structure by 2006
Unit: person (s)
|
Target |
1996 |
2000 |
2006 |
Average growth (%) |
||
|
1997-2000 |
2000-2006 |
1997-2006 |
||||
|
1. Average population |
168,144 |
186,389 |
204,04 1 |
2.08 |
1.83 |
1.95 |
|
+ Urban areas |
5,702 |
6,471 |
6,886 |
2.56 |
1.25 |
1.90 |
|
+ Rural areas |
162,442 |
179,918 |
197,155 |
2.06 |
1.85 |
1.96 |
|
2. Pupulation structure(%) |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
- Urban areas |
3.39 |
3.47 |
3.37 |
|
|
|
|
- Rural areas |
96.61 |
96.53 |
96.63 |
|
|
|
|
3. Gender-based |
168,144 |
186,389 |
204,041 |
2.08 |
1.83 |
1.95 |
|
- Male |
84,600 |
92,207 |
103,312 |
1.74 |
2.30 |
2.02 |
|
++ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Female |
83,544 |
94,182 |
100,729 |
2.43 |
1.35 |
1.89 |
Source: The statistical book of Luc Ngan district from 2000 to 2006
3.2. Labour and employment
The district has a labour force of 116,620 working aged people accounting for 57.16 percent of the population including 92,210 people working in agriculture, forestry and fishery taking 85.96 percent, 3,386 people working in industrial and construction sector accounting for 3.16 percent, 6,550 people working in service sector taking 6.11 percent and 5,126 people working in other sectors accounting for 4.78 percent.
The labour quality has been dramatically improved with 13.5 percent of trained labour in 2006, up 3.1 percent compared to 2001. Thanks to the loan programs and projects, the employment rate and working time in rural areas have been increased (from 71 percent in 2001 to 78 percent in 2006). This is a remarkable figure for a mountainous district in Bac Giang province.
Table 2: Labour development year on year
Unit: person(s)
|
Targets |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
|
Number of labour in the national economy |
93,873 |
95,622 |
97,416 |
99,240 |
101,100 |
102,970 |
|
Number of laboured given jobs per year |
1,716 |
1,749 |
1,794 |
1,824 |
1,845 |
1,870 |
|
Unemployed labour |
26,280 |
24,860 |
23,276 |
21,800 |
20,200 |
18,600 |
|
Rate of using labour time (%) |
71 |
73 |
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 |
|
Rate of trained labour (%) |
10.4 |
10.9 |
11.5 |
12.2 |
13 |
13.5 |
In coming years, the rate of semi-unemployment and sluggish farm workers will increase when the number of people getting into working age is higher than those out of working age. The production and business activities require labour efficiency while it lacks of high-qualified human resources. Appearance of new sectors and careers in line with pressure from competitiveness and advanced science and technology forces the district to make more efforts in dealing with employment issues and training to improve the labour quality as well as attracting talents.
It is essential for the district to pay attention to production development and creating jobs for labourers
These are some key issues the district need to pay attention in coming years:
- Luc Ngan lacks of high-qualified human resources, thus it is difficulties to apply new scientific and technological achievements like informatics, chemistry, biology and technology transfer into production.
- In coming years, with appearance of new sectors and careers in line with pressure from competitiveness and advanced science and technology, the demand for trained labour will be increasing which requires the district to make more efforts in training and talent attraction.
4. Facts of land use structure in the district
According to the land statistics by January 1, 2007,
- The total agricultural land is 63,979.05 hectares accounting for 63.21 percent of the total land area but the land for agricultural production only takes 27.8 percent (only 5.58 percent of land for annual plants and 22.23 percent for perennial plants), forestry land accounts for 35.38 percent while land for aquaculture and other purposes takes small proportion at 0.01 percent.
- The non-agricultural land is 26,689.96 hectares accounting for 26.37 percent of the total natural land area including 18.27 percent of land for special purposes (mainly for national defense with 15.29 percent) and 1.66 percent of residential land.
- The unused land is 10,554.74 hectares accounting for 10.43 percent of the total land area of the district which needs to be exploited in the future.
Therefore, it is necessary to support the locals to re-allocate proper land use structure while exploiting unused land for forestation and fruit tree cultivation. Besides, it needs to change some ineffective land growing corn and cassava to plant fruit trees with high economic efficiency in line with improving fertility of the rice growing area, ensuring sufficient watering and applying high-productivity rice seedlings to meet the food demand.
Table 5: List of soil types in Luc Ngan district as of January 1, 2007
|
No |
TARGET |
Code |
Area (ha) |
Structure (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
|
|
TOTAL NATURAL LAND AREA |
|
101, 223.72 |
100,00 |
|
|
1 |
AGRICULTURAL LAND |
NNP |
63,979.05 |
63.21 |
|
|
1.1 |
Agricultural production land |
SXN |
28,144.83 |
27.80 |
|
|
1.1.1 |
Land for annual plants |
CHN |
5,646.64 |
5.58 |
|
|
1.1.1.1 |
. Land for rice cultivation |
LUA |
5,042.00 |
4.98 |
|
|
1.1.1.2 |
Land for growing grass for livestock |
COC |
40.00 |
0.04 |
|
|
1.1.1.3 |
. Land for annual plants |
HNC(a) |
564.64 |
0.56 |
|
|
1.1.2 |
Land for perennial plants |
CLN |
22,498.19 |
22.23 |
|
|
1.2 |
Forestry land |
LNP |
35,817.85 |
35.38 |
|
|
1.2.1 |
Land for production forest |
RSX |
16,124,04 |
15.93 |
|
|
1.2.2 |
Land for protective forest |
RPH |
19,693.81 |
19.46 |
|
|
1.3 |
Land for fishery |
NTS |
10.97 |
0.01 |
|
|
1.5 |
Other agricultural land |
NKH |
5.40 |
0.01 |
|
|
2 |
NON- AGRICULTURAL LAND |
PNN |
26,689.96 |
26.37 |
|
|
2.1 |
Residential land |
OTC |
1,677.66 |
1.66 |
|
|
2.1.1 |
Rural residential land |
ONT |
1,616.64 |
1.60 |
|
|
2.1.2 |
Urban residential land |
ODT |
61.02 |
0.06 |
|
|
2.2 |
Land for specialized purposes |
CDG |
18,493.91 |
18.27 |
|
|
2.2.1 |
Land for public buildings |
CTS |
49.92 |
0.05 |
|
|
2.2.2 |
Land for national defense and security |
CQA |
15,480.94 |
15.29 |
|
|
2.2.3 |
Land for production and business |
CSK |
20.69 |
0.020 |
|
|
2.2.4 |
Land for public purposes |
CCC |
2,942.36 |
2.91 |
|
|
2.3 |
Land for religious purposes |
Ous TTN |
17.48 |
0.017 |
|
|
2.4 |
Land for cemetery |
NTD |
371.65 |
0.37 |
|
|
2.5 |
Land on the rivers, streams and water surface |
SMN |
6,124.26 |
6.05 |
|
|
2.6 |
Other non-agricultural land |
PNK |
5.00 |
0,00 |
|
|
3 |
UNUSED LAND |
CSD |
10,554.71 |
10,43 |
|
Source: the Natural Resources and Environment of Luc Ngan district